Introduction
What is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a security solution that helps organizations monitor and fix issues in their cloud setups. It ensures that cloud resources, such as storage and databases, are configured correctly and meet security standards. By automating checks and corrections, CSPM reduces the risk of cyberattacks and keeps data safe.
Why Securing Cloud Environments Is Important
Cloud computing has transformed businesses by providing flexibility and scalability. However, this convenience comes with security risks. One of the biggest threats is misconfiguration—when cloud resources are set up incorrectly, leaving sensitive data exposed.
For example, a storage bucket may be left open to the public, making private information accessible to anyone. These errors, though often unintentional, can lead to data breaches, regulatory penalties, and damage to a company’s reputation.
Why CSPM Matters Today
- Increased Cloud Adoption
More businesses rely on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud for their operations. With this growth, ensuring cloud security has become a top priority. - Misconfigurations Are a Common Threat
A significant number of data breaches occur due to simple mistakes in cloud settings. CSPM tools help prevent such issues by continuously scanning for risks and fixing them automatically.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of CSPM
- The Evolution of CSPM
- Key Capabilities of CSPM
- Addressing Common Challenges with CSPM
- Choosing the Right CSPM Tool
- Best Practices for Implementing CSPM
- Real-World Applications and Use Cases
- Future Trends in CSPM
- Conclusion
1.Understanding the Basics of CSPM
1.1 What is CSPM?
Definition and Key Features
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) refers to a set of tools and practices designed to ensure cloud environments are configured securely and remain compliant with industry standards. It focuses on detecting and fixing misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and potential risks in cloud infrastructure.1
Key features of CSPM include:
- Continuous Monitoring: Tracks cloud resources in real-time to identify misconfigurations or policy violations.
- Automated Remediation: Fixes security issues automatically to maintain compliance and reduce manual workload.
- Compliance Management: Ensures adherence to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS by monitoring cloud environments against predefined standards.
- Multi-Cloud Support: Provides security across multiple cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
How CSPM Differs from Traditional Security Tools
Unlike traditional security tools that focus on protecting networks and endpoints, CSPM is purpose-built for the dynamic nature of cloud environments. While firewalls and antivirus solutions work to block threats, CSPM:
- Focuses on misconfiguration prevention rather than reactive threat detection.
- Provides visibility into cloud-specific risks, such as insecure storage or excessive permissions.
- Operates seamlessly across multi-cloud setups, where traditional tools often struggle.
1.2 Why is CSPM Essential?
Addressing the Challenges of Cloud Misconfigurations
Misconfigurations are the leading cause of cloud security breaches. For example, leaving a storage bucket publicly accessible or failing to encrypt sensitive data can expose organizations to significant risks2. CSPM addresses these issues by:
- Scanning for misconfigurations continuously.
- Providing detailed reports and suggestions for remediation.
- Automatically correcting common errors.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Many industries must comply with strict regulations to protect sensitive data, such as healthcare (HIPAA) or finance (PCI DSS). CSPM simplifies compliance by:
- Mapping cloud configurations against regulatory requirements.
- Generating audit-ready reports.
- Alerting users to potential non-compliance issues before they become a problem.
Enhancing Cloud Visibility and Control
Cloud environments can quickly become complex, with resources spread across multiple providers. CSPM tools provide:
- Unified Dashboards: A centralized view of all cloud resources, their configurations, and associated risks.
- Access Management: Insights into who has access to what, reducing the likelihood of insider threats.
- Policy Enforcement: Ensures that security policies are applied consistently across all resources.
2.The Evolution of CSPM
2.1 The Origins of CSPM
Historical Context: Challenges of Manual Cloud Security Management
When cloud computing began to gain traction, securing cloud environments was a largely manual process. IT teams relied on static security tools and periodic audits, which were often ineffective in dynamic cloud environments. Key challenges included:
- Lack of Visibility: IT teams struggled to track and monitor rapidly changing cloud resources.
- Error-Prone Processes: Manual configuration checks often missed critical misconfigurations, leading to security gaps.
- Scalability Issues: Traditional tools couldn’t scale effectively as organizations adopted multi-cloud strategies.
These challenges highlighted the need for an automated approach to monitor and manage cloud configurations continuously.
Initial Focus on Configuration Monitoring
The first generation of CSPM tools emerged to address these issues by automating the monitoring of cloud configurations. Early CSPM solutions primarily focused on:
- Detecting misconfigurations, such as open storage buckets or weak authentication settings.
- Ensuring configurations aligned with predefined security baselines.
- Alerting administrators to security risks in near real-time
2.2 How CSPM Has Evolved
Integration with AI/ML for Predictive Analytics
Modern CSPM solutions leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to go beyond detecting misconfigurations. These technologies enable:
- Risk Prediction: Identifying potential vulnerabilities before they become threats.
- Threat Prioritization: Ranking risks based on their severity, allowing teams to focus on critical issues first.
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitoring patterns to detect anomalous activity indicative of a security breach.
Support for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
As organizations adopt multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, CSPM tools have evolved to manage security across diverse environments. Key advancements include:
- Unified Security Views: Providing a single pane of glass to monitor resources across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and on-premises systems.
- Interoperability: Ensuring consistent security policies and controls across different platforms.
Advanced Automation and DevOps Alignment
Modern CSPM tools integrate seamlessly with DevOps workflows, embedding security into Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Features include:
- Automated Security Checks: Running compliance checks during development and deployment phases.
- Policy-as-Code: Allowing developers to define and enforce security policies programmatically.
- Incident Response Automation: Automatically remediating issues without manual intervention, reducing time-to-resolution.
3.Key Capabilities of CSPM
3.1 Visibility and Monitoring
Providing Real-Time Insights into Cloud Assets
CSPM tools offer a centralized view of all cloud resources, such as servers, databases, and storage buckets, across multiple cloud providers. This visibility allows organizations to:
- Identify which resources are in use.
- Understand their configurations and associated risks.
- Detect unauthorized changes in real-time.
Detecting Misconfigurations and Vulnerabilities
CSPM tools continuously scan for common security issues like:
- Open storage buckets.
- Excessive permissions granted to users or services.
- Outdated or missing encryption on data.
By detecting these issues early, CSPM helps prevent breaches caused by misconfigurations, which are among the top causes of cloud security failures.
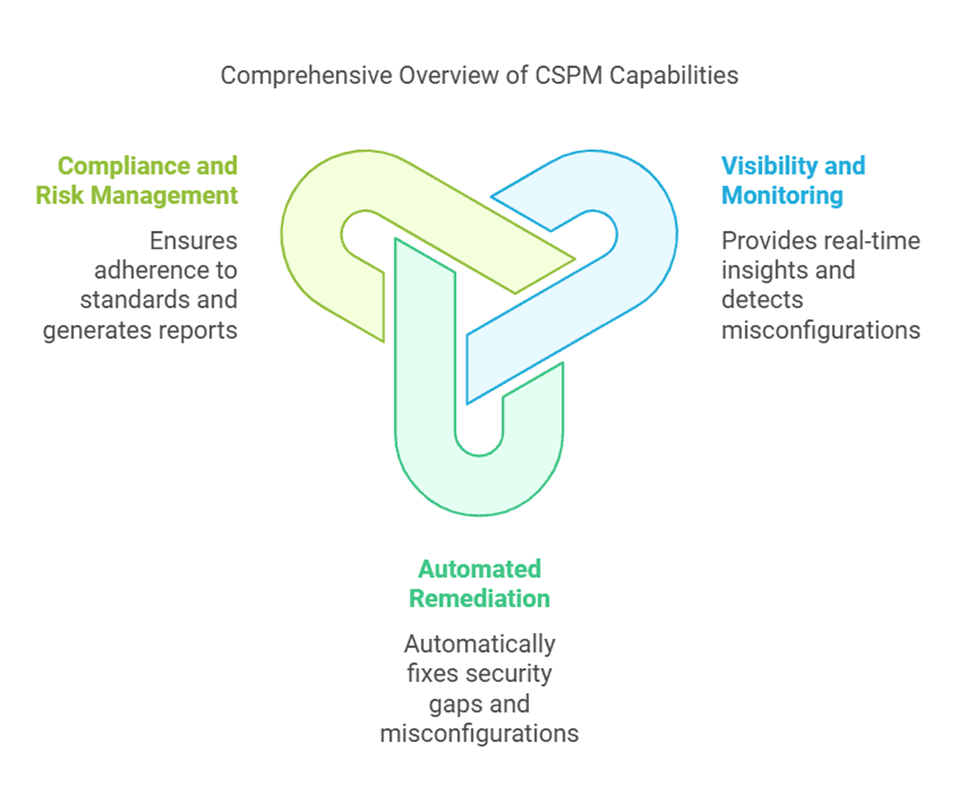
3.2 Automated Remediation
How Automation Fixes Security Gaps Efficiently
One of the most powerful features of CSPM is its ability to automatically correct misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. This automation reduces the manual effort required by IT teams and minimizes the time during which resources are left exposed.
Examples of Common Issues CSPM Tools Resolve
- Publicly Accessible Resources: Automatically restricting access to storage buckets or databases that are unintentionally exposed to the public.
- Weak Password Policies: Enforcing strong authentication mechanisms, like multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Non-Encrypted Data: Enabling encryption for data at rest and in transit to comply with security best practices.
These automated fixes ensure that organizations can maintain a secure posture even as their cloud environments grow more complex.
3.3 Compliance and Risk Management
Monitoring Frameworks Like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001
CSPM tools are equipped with prebuilt templates to monitor compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as:
- GDPR: Ensuring proper data privacy controls for EU residents.
- HIPAA: Protecting sensitive health information.
- ISO 27001: Maintaining an information security management system.
Generating Reports for Audits and Continuous Compliance
CSPM simplifies compliance by automatically:
- Generating detailed reports that demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Highlighting areas of non-compliance for immediate action.
- Maintaining continuous monitoring to ensure organizations stay compliant between formal audits.
Addressing Common Challenges with CSPM
4.1 Securing Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Challenges of Managing Diverse Cloud Platforms
Organizations increasingly use a mix of cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, along with on-premises systems. While this multi-cloud and hybrid approach offers flexibility, it introduces several challenges:
- Lack of Unified Security: Each platform has unique configurations, making consistent security policies difficult to implement.
- Visibility Issues: Tracking resources and identifying risks across different environments can be overwhelming.
- Inconsistent Compliance: Adhering to regulatory standards becomes complex when multiple providers are involved.
How Cloud Security Posture Management Ensures Consistent Security Across Clouds
CSPM tools are designed to provide a unified security framework across diverse environments. They:
- Offer centralized dashboards to monitor all resources, regardless of the cloud provider.
- Standardize security policies and enforce them uniformly across platforms.
- Automate compliance checks for multiple frameworks, ensuring consistent regulatory adherence across environments.
4.2 Bridging the Gap with DevOps
Aligning CSPM with CI/CD Pipelines
Modern development cycles rely heavily on Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Without proper integration, cloud security posture management can lag behind fast-paced development. CSPM tools address this by:
- Running real-time security checks during code deployment to identify vulnerabilities.
- Providing feedback to developers early in the pipeline, reducing the cost and time of fixing issues.
Enabling DevSecOps Practices
CSPM tools support the shift-left approach, integrating security into every stage of the development process. They enable DevSecOps by:
- Enforcing Policy-as-Code, allowing developers to define and apply security policies programmatically.
- Automating incident response, ensuring that issues identified during development are resolved promptly.
4.3 Avoiding Overreliance on Automation
The Importance of Human Oversight
While automation is a key strength of cloud security posture management, overreliance on it can lead to blind spots. Automated tools may not:
- Fully understand the context of certain security policies.
- Handle edge cases or nuanced risks effectively.
Human oversight is essential to:
- Interpret complex security scenarios.
- Adjust policies to align with organizational goals.
- Validate automated fixes to prevent unintended consequences.
Best Practices for Balancing Automation and Manual Checks
- Review Automated Reports Regularly: Ensure that alerts and fixes align with broader security objectives.
- Customize Security Policies: Tailor automated rules to the unique needs of your organization.
- Combine Tools with Expertise: Use CSPM to handle routine tasks while allowing security teams to focus on strategic decisions.
Choosing the Right CSPM Tool
5.1 Key Factors to Consider
Selecting the right Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tool is crucial for securing your cloud environment. Here are the key factors to evaluate:
1. Multi-Cloud Compatibility
Many organizations use multiple cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. A robust CSPM tool should:
- Provide unified security management across all platforms.
- Standardize policies and configurations regardless of provider differences.
- Offer comprehensive visibility into multi-cloud and hybrid environments.
2. Ease of Integration with Existing Workflows
Seamless integration with your organization’s tools and processes ensures smoother adoption. Look for CSPM tools that:
- Integrate with CI/CD pipelines and DevOps tools for a shift-left approach to security.
- Support existing Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
- Offer APIs for customization and easy integration with in-house tools.
3. Cost and ROI Considerations
CSPM tools can range in cost, so it’s important to assess the value they provide:
- Licensing and Subscription Costs: Evaluate whether the tool fits within your budget.
- Time and Effort Saved: Measure the reduction in manual labor through automation.
- Compliance Benefits: Calculate potential savings from avoided penalties due to non-compliance.
5.2 Comparing Top CSPM Tools
Here’s an overview of some leading CSPM tools, their strengths, and unique features:
1. Prisma Cloud (by Palo Alto Networks)
- Strengths: Comprehensive multi-cloud support and advanced threat detection.
- Key Features:
- Automated compliance checks for frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Integration with DevOps workflows and CI/CD pipelines.
- AI-driven risk prioritization to address critical issues first.
- Best For: Organizations looking for a feature-rich, scalable solution.
- Reference: Palo Alto Networks: Prisma Cloud
2. Wiz
- Strengths: Intuitive interface and deep visibility into cloud environments.
- Key Features:
- Identifies risks across all layers of the cloud, from infrastructure to applications.
- Supports multi-cloud environments with a unified view.
- Rapid deployment without requiring agents.
- Best For: Teams needing quick deployment and enhanced risk visualization.
Zscaler CSPM
- Strengths: Strong focus on compliance and policy enforcement.
- Key Features:
- Automated remediation of misconfigurations.
- Centralized dashboard for monitoring multi-cloud setups.
- Real-time policy enforcement to prevent security lapses.
- Best For: Enterprises prioritizing compliance management.
Best Practices for Implementing CSPM
6.1 Conduct a Gap Analysis
To effectively implement Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), start by identifying existing weaknesses in your cloud environment.
- Assessing Current Cloud Security Posture:
- Review all cloud resources to determine their configurations and usage.
- Map out potential exposure points, such as public access to sensitive resources.
- Identifying Vulnerabilities and Compliance Gaps:
- Use CSPM tools to scan for misconfigurations, missing encryption, and weak access controls.
- Check compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
Actionable Tip: Prioritize risks based on their severity and impact, and address critical issues first.
6.2 Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
- Customizing CSPM Rules for Organizational Needs:
- Define security policies tailored to your business, such as who can access sensitive data or what constitutes secure configurations.
- Use CSPM’s policy-as-code feature to enforce these rules programmatically.
- Regularly Updating Policies:
- Cloud environments are dynamic, and policies must evolve alongside new applications, technologies, and threats.
- Schedule regular reviews to ensure rules align with industry standards and organizational changes.
Actionable Tip: Document and communicate policies across teams to ensure consistency.
6.3 Train Your Teams
- Educating IT and DevOps Teams on CSPM Capabilities:
- Offer training on how CSPM tools work, including dashboards, alerts, and automated remediation.
- Emphasize the importance of security in DevOps workflows.
- Promoting a Culture of Continuous Security Improvement:
- Encourage teams to proactively identify risks and adopt best practices.
- Recognize and reward efforts to maintain a secure cloud environment.
Actionable Tip: Leverage CSPM tools to provide real-time feedback to teams, helping them learn from incidents and improve.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
7.1 Incident Response Optimization
CSPM tools significantly improve incident response by:
- Real-Time Alerts: Notifying teams instantly of misconfigurations or potential breaches.
- Automated Remediation: Fixing issues like open storage buckets or excessive permissions before attackers exploit them.
- Damage Reduction: Minimizing downtime and impact by identifying and resolving incidents faster.
Example: A misconfigured cloud database exposing sensitive customer data can be identified and secured within minutes using CSPM.
7.2 Industry-Specific Examples
- CSPM in Healthcare:
- Ensures compliance with HIPAA by monitoring for violations like unencrypted patient records or improper access controls.
- Provides audit-ready reports to demonstrate regulatory adherence.
- CSPM in Finance:
- Mitigates risks under PCI DSS by enforcing encryption for payment data and monitoring for unauthorized access to financial systems.
- Protects sensitive customer information from exposure due to misconfigurations.
Future Trends in CSPM
8.1 AI and Machine Learning Advancements
- Predictive Risk Detection Using AI:
- Leveraging AI to analyze patterns and predict vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Identifying anomalies in real-time to enhance threat detection.
- Enhanced Decision-Making with Machine Learning:
- ML algorithms prioritize risks based on severity, helping teams focus on critical issues.
- Adaptive learning continuously improves accuracy and efficiency over time.
8.2 Expanding Role in Edge Computing
- Addressing Security Challenges in Edge Devices:
- As edge computing grows, CSPM tools are adapting to secure data and devices beyond traditional cloud environments.
- Real-time monitoring of edge nodes ensures they comply with security policies.
- Example: Securing IoT devices connected to cloud platforms to prevent data leaks or unauthorized access.
8.3 Integration with Quantum-Safe Security
- Preparing for Cryptographic Challenges:
- As quantum computing advances, traditional encryption methods may become vulnerable.
- CSPM tools are expected to integrate quantum-resistant algorithms to protect cloud environments.
- Future-Ready Security: Organizations using CSPM will be better equipped to adapt to cryptographic changes and protect sensitive data.
Conclusion
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is essential for securing modern cloud environments by preventing misconfigurations, ensuring compliance, and enhancing visibility across multi-cloud and hybrid setups. As cloud adoption grows, leveraging CSPM helps organizations proactively address security risks and safeguard sensitive data. Start by assessing your current cloud security posture to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. Explore tools like Prisma Cloud, Wiz3, or Zscaler4 to find the solution that fits your needs and take the first step toward a secure and resilient cloud infrastructure.
References:
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/Cloud-Security-Posture-Management-CSPM ↩︎
- https://www.zscaler.com/resources/security-terms-glossary/what-is-cloud-security-posture-management-cspm ↩︎
- https://www.wiz.io/academy/what-is-cloud-security-posture-management-cspm ↩︎
- https://www.zscaler.com/resources/security-terms-glossary/what-is-cloud-security-posture-management-cspm ↩︎