Introduction
What is BIOS?
When you turn on your computer, it doesn’t just magically start working. That’s where the BIOS—short for Basic Input/Output System—comes in. BIOS is the first piece of software your computer runs when you press the power button.1 It checks your hardware, makes sure everything is working, and then helps your computer boot up by handing control over to the operating system. Without the BIOS, your computer wouldn’t even know where to begin!
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Phoenix Technologies
- Historical Context of Phoenix BIOS
- Key Features of Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG
- Practical Guidance for Tech Enthusiasts: Working with Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG (10-04-2012)
- The Transition from BIOS to UEFI
- The Value of Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG: Skills and Insights
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
Introduction to Phoenix Technologies
If you’ve ever heard of BIOS, chances are you’ve also heard of Phoenix Technologies. Founded in 1979, this company has played a huge role in the development of computer firmware. They created BIOS systems that made personal computers more reliable and easier to use, becoming a key part of computing history.
One of their most notable achievements was the release of Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG BIOS on 10-04-2012. This version became popular in many older systems thanks to its flexibility and ability to support a wide range of hardware.
Why Focus on Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG?
The Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG2, released on 10-04-2012, wasn’t just another software update. It was a crucial tool for keeping older computers running smoothly during a time when technology was changing rapidly. This BIOS version stood out because of its ability to support legacy systems, giving older hardware a second life.
Talking about Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG helps us understand how important BIOS technology was in making computers what they are today. It’s a great way to explore the role firmware has played in connecting hardware and software—and how it paved the way for modern advancements like UEFI.
Historical Context of Phoenix BIOS
The Evolution of BIOS Technology
The BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, has been an essential part of computing since its inception in the late 1970s.3 It acts as the bridge between a computer’s hardware and software, ensuring the system is ready to boot.
Key Milestones in BIOS Development:
- 1975: IBM introduced the first BIOS with its PC, setting the foundation for all future computers.
- 1981: The first open BIOS appeared, allowing third-party companies to develop compatible hardware and firmware.
- 1990s: BIOS became more sophisticated, supporting advanced configurations like power management and plug-and-play devices.
- 2000s: BIOS began to decline in popularity as newer technologies like UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) started to emerge, offering more capabilities.
How Phoenix Technologies Contributed to These Advancements
Phoenix Technologies played a pivotal role in shaping BIOS technology. The company, founded in 1979, was one of the first to develop third-party BIOS solutions for non-IBM computers. This innovation helped establish the PC as an open platform, allowing various manufacturers to build compatible hardware.
Some of Phoenix’s key contributions include:
- 1984: Phoenix Technologies introduced the first commercially available BIOS for clone PCs, ensuring compatibility and standardization.
- 2000s: The company’s firmware solutions, like Phoenix SecureCore, supported advanced features such as security protocols and power-saving configurations, laying the groundwork for modern systems.
Overview of the 6.00PG Version
Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, released on 10-04-2012, marked a significant step forward in legacy system support. This version was known for:
- Wide Compatibility: It worked seamlessly with a variety of hardware configurations, making it a favorite among manufacturers.
- Flexibility: Users could modify boot priorities, manage system settings, and troubleshoot errors easily through an intuitive interface.
- Stability: This version was particularly valued for its reliability, making it a go-to solution for older systems.
Why It Became a Standard for Many Systems
During the early 2010s, many systems relied on the Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG because it struck a perfect balance between compatibility and performance. While newer technologies like UEFI were emerging, this BIOS version ensured that older hardware could remain functional, delaying the need for costly upgrades.
Relevance Today:
Even in 2025, enthusiasts and professionals working with retro systems often encounter Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG. Its robust design and ease of use make it a timeless piece of technology.
Key Features of Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG
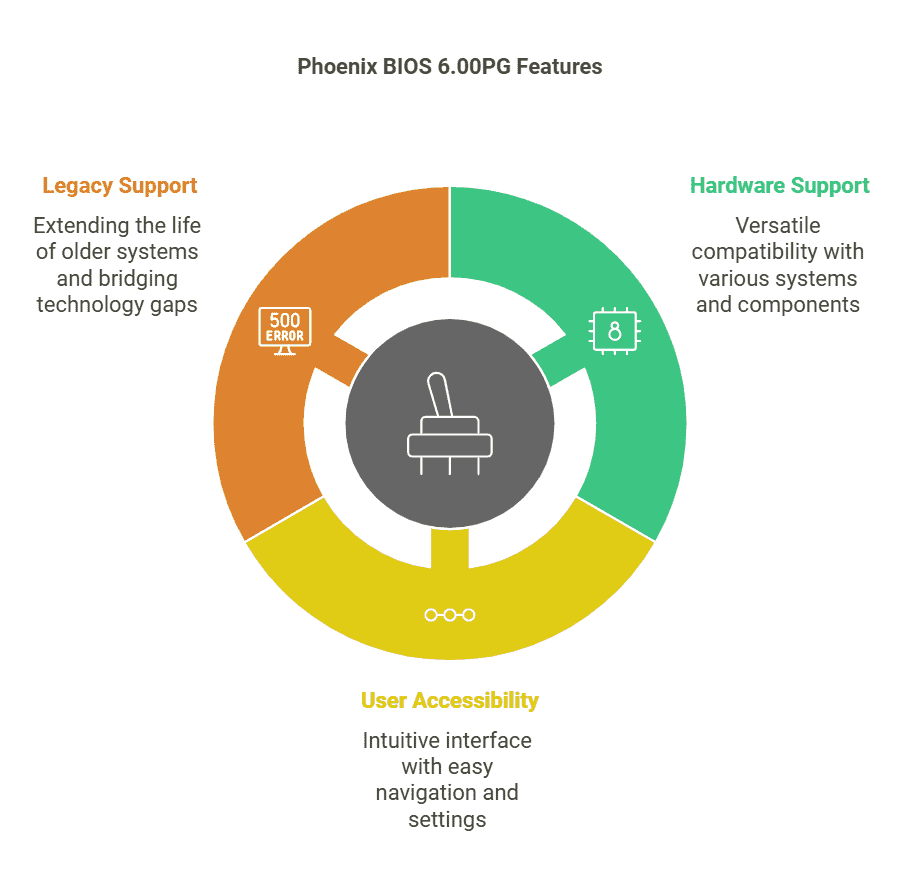
Functionality and Compatibility
The Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, released on 10-04-2012, was designed to cater to a broad range of systems, ensuring seamless functionality and compatibility.
- Supported Hardware Platforms:
- The 6.00PG version was versatile, supporting various processors, memory configurations, and storage devices.
- Its compatibility with legacy components made it ideal for older desktops, servers, and industrial systems still in use during the 2010s.
- Reliability and Flexibility:
- Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG was known for its stability, a critical feature for systems requiring consistent uptime.
- Its flexible configuration options allowed users to tweak system settings to optimize performance for specific applications.
User Accessibility
One of the standout features of Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG was its user-friendly design.
- Intuitive BIOS Setup Utility:
- The BIOS interface was straightforward, with clearly labeled menus that made it easy for users to navigate and adjust settings.
- Unlike some earlier BIOS versions, it included detailed descriptions for settings, helping users understand their choices.
- Key Settings Users Could Modify:
- Boot Order: Allowed users to prioritize devices like hard drives, optical drives, or USBs for booting.
- Power Management: Enabled features like energy-saving modes and wake-on-LAN.
- Hardware Monitoring: Provided real-time data on CPU temperature, fan speeds, and voltages for better system management.
Legacy System Support
Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG played a crucial role in extending the life of older hardware systems, which was essential during an era of rapid technological change.
- Prolonged Usability:
- By supporting legacy devices and components, the BIOS allowed older systems to remain operational, reducing the need for immediate hardware upgrades.
- This was particularly valuable for industries relying on specialized equipment that could not be replaced easily.
- Bridging the Gap:
- The BIOS acted as a bridge between older hardware and newer operating systems, ensuring compatibility and functionality.
Practical Guidance for Tech Enthusiasts: Working with Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG (10-04-2012)
Accessing the BIOS
Accessing the Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG setup utility is straightforward. Follow these steps:
- Restart Your Computer:
- During the boot process, keep an eye out for a message like “Press DEL to enter setup” or “Press F2 for BIOS.”
- Press the Key Prompted:
- Common keys to access Phoenix BIOS include DEL, F2, or F10. The specific key depends on your motherboard model.
- Enter the BIOS Setup Utility:
- Once inside, you’ll see menus for configuring various system settings.
Configuring Common Settings
The Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG BIOS allows you to customize your system for optimal performance. Here’s how:
- Changing Boot Priorities:
- Navigate to the Boot Order menu.
- Select the device (e.g., hard drive, USB drive, or CD/DVD) you want to boot from first.
- Save changes and exit.
- Adjusting CPU or Memory Settings:
- Go to the Advanced Settings menu.
- Modify CPU frequency or enable overclocking features (if supported).
- Adjust memory timings to optimize performance.
- Managing Power-Saving Features:
- Head to the Power Management section.
- Enable options like Sleep Modes, Hibernate, or Wake-on-LAN to conserve energy.
Updating BIOS Firmware
Keeping your BIOS updated is crucial for compatibility and security.
- When and Why to Update:
- Update your BIOS if you encounter hardware compatibility issues or need new features.
- 4Avoid updating unnecessarily, as this can introduce risks.
- Risks Involved:
- A failed update can render your system unbootable.
- Ensure you have a stable power supply and follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely.
- How to Perform Updates Safely:
- Visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website for the correct BIOS update file.
- Use tools provided by Phoenix Technologies or your motherboard vendor to flash the new BIOS.5
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Error Messages During POST (Power-On Self-Test):
- POST errors can indicate hardware problems or incorrect settings.
- Common solutions:
- Reseat RAM and other components.
- Restore BIOS to default settings.
- Solutions for Common BIOS-Related Problems:
- System Won’t Boot: Verify boot device order and hardware connections.
- Overheating Issues: Check CPU fan speed settings and thermal paste application.
The Transition from BIOS to UEFI
Understanding UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface)
UEFI, or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, is the modern successor to traditional BIOS. It was developed as a more robust and flexible system to handle the growing complexities of modern hardware and software.
Unlike BIOS, which operates in 16-bit real mode and is limited in functionality, UEFI leverages 32-bit or 64-bit environments, providing a more powerful interface. It comes with a graphical user interface (GUI) and supports mouse navigation, making it far more user-friendly than the text-based BIOS.
How UEFI Differs from Traditional BIOS6
Here are the key differences between UEFI and BIOS:
| Feature | BIOS | UEFI |
| Bit Support | 16-bit | 32-bit or 64-bit |
| Boot Mode | Legacy (MBR-based) | Modern (GPT-based) |
| User Interface | Text-only | Graphical (mouse support) |
| Boot Time | Slower | Faster |
| Disk Support | Limited to 2TB (MBR) | Supports disks >2TB (GPT) |
| Extensibility | Limited | Highly extensible (drivers, apps) |
Advantages of UEFI
UEFI offers several improvements over BIOS, including:
- Faster Boot Times:
- UEFI streamlines the boot process, reducing startup time significantly.
- Support for Larger Disks:
- UEFI uses the GUID Partition Table (GPT), enabling support for disks larger than 2TB, a limitation in BIOS.
- Secure Boot:
- UEFI includes Secure Boot, a security feature that prevents unsigned or malicious software from loading during the boot process.
- Extensibility:
- With UEFI, you can add custom drivers and applications to the firmware, making it highly adaptable to different needs.
- Compatibility with Modern Systems:
- UEFI is designed to work seamlessly with modern hardware architectures and operating systems.
The Value of Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG: Skills and Insights
Why Learn About Legacy BIOS Systems?
Legacy BIOS systems, like Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, are more than just old firmware—they represent the foundation of modern computing. Exploring these systems offers valuable insights for tech enthusiasts eager to understand how current technologies evolved and how they can apply this knowledge.
- Understanding Foundational Technologies:
- Legacy BIOS systems introduced essential processes like hardware initialization and the Power-On Self-Test (POST), which are still relevant today.
- By learning how Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG operates, enthusiasts can gain a deeper understanding of the principles underlying modern firmware like UEFI.
- Retro Computing and Hardware Restoration:
- Vintage systems often rely on BIOS firmware to function, and many hobbyists are dedicated to restoring and preserving these machines.
- Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, released on 10-04-2012, remains a critical tool for maintaining older PCs, allowing enthusiasts to relive and preserve the computing experience of that era.
Future-Proofing Skills
Studying legacy BIOS systems doesn’t just provide historical knowledge—it equips tech enthusiasts with skills that can be applied to modern computing challenges.
- Building Transferable Skills:
- The troubleshooting techniques and configuration knowledge gained from working with systems like Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG directly translate to managing modern firmware environments like UEFI.
- Understanding boot sequences, hardware prioritization, and firmware updates builds a solid foundation for tackling advanced computing tasks.
- Developing Diagnostic Expertise:
- Legacy BIOS systems require a hands-on approach to problem-solving, such as interpreting POST codes or reconfiguring hardware settings.
- These skills remain valuable in IT fields where debugging and system optimization are critical.
- Appreciating Security Evolution:
- Older systems relied on basic security measures, such as BIOS passwords. By comparing these to modern advancements like Secure Boot, enthusiasts can better understand the evolution of system security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG?
Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, released on 10-04-2012, is a firmware solution developed by Phoenix Technologies to manage hardware initialization and boot processes. It was widely used in legacy systems for its reliability and compatibility. (For more details, see the section “Historical Context of Phoenix BIOS.”)
2. Is it still possible to use systems with this BIOS version?
Yes, systems with Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG can still operate, especially for retro computing or specific industrial applications. However, they may not support modern hardware or security standards.
3. How do I update or replace an old BIOS?
Updating or replacing an old BIOS requires downloading the correct update from the manufacturer and flashing it carefully. (Refer to “Practical Guidance for Tech Enthusiasts” for detailed steps.)
4. What is the difference between Phoenix BIOS and UEFI?
UEFI replaces traditional BIOS with advanced features like Secure Boot, graphical interfaces, and support for large disks. (See “The Transition from BIOS to UEFI” for an in-depth comparison.)
Conclusion
Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG, released on 10-04-2012, stands as a significant milestone in the evolution of computing. It provided a reliable and adaptable firmware solution during a time when legacy systems were still widely used, bridging the gap between older hardware and emerging technologies. This BIOS version played a crucial role in extending the lifespan of many systems, making it a valuable tool for industries, educational institutions, and retro computing enthusiasts.
Learning about systems like Phoenix Technologies 6.00PG helps us appreciate the foundational technologies that shaped modern computing. It not only enriches our understanding of how far we’ve come but also equips us with skills applicable to modern firmware like UEFI. Preserving and exploring these legacy systems is not just about nostalgia—it’s about honoring the history of technology and learning valuable lessons for the future. We’d love to hear from you! Share your experiences working with Phoenix BIOS 6.00PG or any legacy systems in the comments below. If you have questions about updating or
References:
- https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/b/bios.htm? ↩︎
- https://www.phoenix.com/about/? ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phoenix_Technologies? ↩︎
- TrishTech ↩︎
- https://forums.tomshardware.com/threads/how-to-update-phoenix-award-bios-v6-00pg.1383959/ ↩︎
- https://www.thewindowsclub.com/difference-between-bios-and-uefi? ↩︎