Information Technology Definition
Information technology is a process in which different systems are involved in storing, managing, and transmitting data in computers and other devices.
Information technology has become an important part of today’s digital world. Information technology is the main part of modern applications in communication, businesses operations, data analysis and security systems. Information technology system primarily consists of hardware, software, and other related devices which are operated by group of information technology users. A comprehensive IT system is the backbone of many organizations for management of important tasks like data management, communication networks, and overall organizational processes.
Table of Contents
History of Information Technology
Early Foundations (Pre-20th Century)
[3000 BCE]: Ancient Mesopotamians developed the abacus1, which is one of the earliest known tools for calculation.
[1600-1800]: Blaise Pascal created mechanical calculators and Charles Babbage designed the Difference Engine2, which set the groundwork for computation.
[1840]: Ada Lovelace wrote the first algorithm for Babbage’s Analytical Engine. She is one of earliest computer programmers.
Birth of Modern Computing (1930s-1940s)
[1936]: Alan Turing conceptualized the “Universal Machine3”. This was a theoretical model for general-purpose computer that influenced future developments.
[1941]: Konrad Zuse built the Z3, the world’s first programmable and fully automatic digital computer.
[1945]: Electrical Numerical Integrator and Computer was invented and it was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer. It was used for military calculations during World War II.
The Rise of Computers (1950s-1960s)
[1951]: Universal Automatic Computer, the first commercially available computer for people.
[1956]: IBM introduced IBM 305 RAMAC.4 with first hard disk drive. This invention introduced the new era of digital information storage and foundation for information technology.
[1960s]: IBM evolved its computer in mainframe shapes and different businesses and companies started adopting computing systems.
The Microprocessor Revolution (1970s)
[1971]: Intel released 4004 microprocessors, which created more smaller and affordable computers.
[1975]: Altair 88005 a popular early microcomputer was invented and Bill Gates and Paul Allen founded Microsoft to create software for it.
[1976]: Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak founded Apple Computer and introduced Apple I, one of the first personal Computers.
The Personal Computer (PC) Boom (1980)
[1981]: IBM launched IBM PC, after this launch computers were widely accessible for home and business use.
[1984]: Apple launched Macintosh, which is better know for its graphical user interface.
[1980]: During this time, word processing and spreadsheets were invented which transformed business operations.
The internet and Network Revolution(1990s)
[1991]: Tim Berners-Lee6 Invented the world wide web, which allowed user to access information via internet.
During 1990, Easy internet access and emails changed the communication and information sharing and storage.
[1999]: Wi-fi emerged and marked the beginning of wireless networking and set the foundation for mobile computing.
The Mobile and Cloud Era (2000-2010s)
[2000]: Broadband became widely available and internet speed increased, which fostered the growth of social media and e-commerce.
[2007]: Apple introduced the iPhone, popularizing smartphones and applications which revolutionized the spectrum of information technology.
[2010]: Rise of cloud computing services like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure, which transformed the infrastructure of IT for businesses.
Modern Information Technology and Emerging Technologies
[2020]: Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning was integrated into modern devices and applications.
- Industries started adopting blockchain and 5G technology enabling more faster IT operations.
- Today is IT continuously evolving, with more focus upon data privacy and cybersecurity. Information technology has been integrated in all branches of technology including AI, Software and VR. Information technology is playing a foundational role in digitally interconnected world.
Why is Information Technology Important in Today’s World?
Information technology is the backbone of modern communication systems. It is a technology which is integral part of almost every industry and system which is involved in day-to-day functioning of modern world.
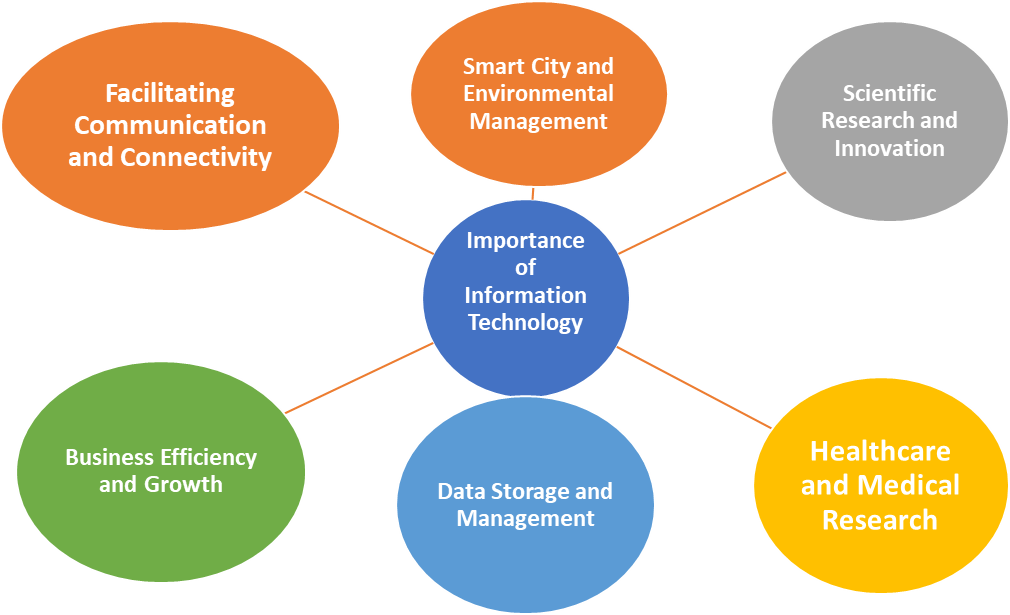
Facilitating Communication and Connectivity
Information technology enables instant communication across the globe.IT has allowed fast communication via different sources including, email, video conferencing, social media, and other online platforms. Information technology has also revolutionized personal and business communications very fast, helping in maintaining global communication very easy.
Business Efficiency and Growth
Businesses who rely on IT systems for their operations, can manage their tasks and operation very easily. They can manage complex tasks like inventory, payroll, and data analysis very easily through software and cloud platforms.
Data Storage and Management
Information Technology has revolutionized the data storage and management process. Now companies can store large amount of data in a well organized and classified manner. Companies can access any data any time with simple clicks. Information technology has also eliminated the risk of data loss because it is saved on secure cloud system. Data reading, processing and sharing has become very easy and fast.
Education and Skill Development
Information technology is important, as it has made education accessible to people worldwide. IT has provided E-learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and online courses which are very helpful for students learn education from their homes. Digital text-books, digital marketing platforms, and other tech platforms from IT has enabled people to learn online skills and earn money.
Healthcare and Medical Research
IT has introduced telemedicine, patient records, and data management in healthcare system. With IT systems health care patients can consult with patients remotely. With increased accessibility to medical services. Remote consultancy is very beneficial for rural area patients and electronic health records provides complete patient history and record with one click.
Scientific Research and Innovation
IT facilitates scientific research by enabling researchers to process large datasets. With IT researches can collaborate globally with their colleagues and can accelerate their efforts in scientific fields. Information technology integrations are also important part of new technologies like Internet of things, Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity.
Smart City and Environmental Management
IT systems are also facilitating in infrastructure development of Smart Cities. IT is helping in traffic management, energy distribution and waste management, helping in overall functioning of modern cities. IT enables real-time environment monitoring and helps governments and organization to address climate change and pollution issues.
Types of Information Technology
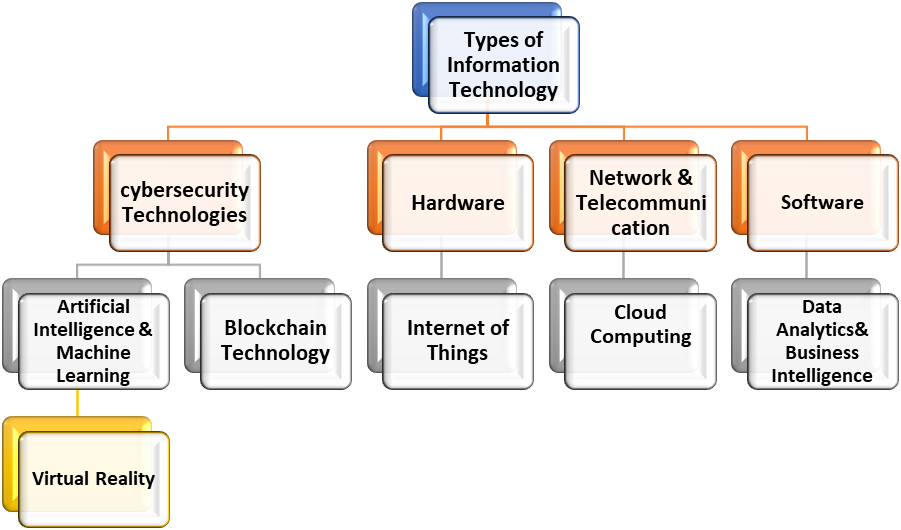
Information Technology is a vast field, it is part of different technologies in various shapes. Following are the important types of Information technology.
Hardware
Information technology can be seen in infrastructure of computer, servers, mainframes, hard drives, and Solid-state drives (SSDs). Similarly, internet routers, modems, and wireless access points are example of information technology in hardware shape.
Software
In software shape information technology is can be seen in Windows, macOS, Linux and provide foundation for applications on computer servers. Similarly, word processors, spreadsheets, media players are another type of information technology. Software form of IT includes CRM software, ERP, and supply chain management software which helps in business operations.
Networking and Telecommunication
Networking and telecommunication are another type of information technology. Wide area networks, wireless technologies, 4G, 5G and satellite essential part of mobile phones.
Data Management
Information technology is important part of data management systems. Rational database, NoSQL database, and data warehousing systems are based on information technology.
Cybersecurity Technologies
Cybersecurity is the prime need of modern online businesses, and information technology is present in cybersecurity is a different shape. Information technology can be seen in cybersecurity firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus and anti-malware software and encryption techniques.
Cloud Computing
Information technology is the important part of cloud computing. Cloud computing provides servers and storage and data management on virtual computers on internet.
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Information technology is present in data analytics application and business intelligence platforms. These applications provide business intelligence services by monitoring trends and market insights.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Latest technological advancement artificial intelligence and machine learning are also a type of Information technology. In this type IT enables machines to learn and mimic like humans.
Internet of Things
IT is present in a different shape in all smart devices, appliances, wearable gadgets, and home appliances.
Blockchain Technologies
Modern blockchain technology like cryptocurrency, smart contracts, and online trade systems are based upon information technology.
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality are also using information technology and IT is present in these latest technologies in a different type. With Information technology applications, VR and AR are also expanding in new fields like real estate and retail.
Informational Technology Degree, Careers and Certificates
Informational Technology Degree
Information technology degree provides the information which is required to understand and manage security systems. IT degree is valid for technology related jobs in business organization, technology institutions, healthcare, and other enterprises.
During IT degree students learn essentials skill like programming where they develop coding abilities. Students learn different coding languages like python and Java. These coding skills are essential for software development life cycle.
IT degree also cover information security, a vital part of safeguarding digital information against cyber threats. IT students also study best practices in cybersecurity and learn how to protect data and main systems.
IT degree includes Network Administration which enables IT students to manage computer networks. This part of the degree involves studying network architecture, troubleshooting issues and learning about network setup and maintenance.
Careers in Information Technology and Certificates Required are as follows
Software Development and Engineering
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Software Developer, Web Developer, Mobile Application developer, Full-Stack Developer | Creating Applications, websites, mobile solutions, coding, testing, debugging software, working with database and APIs | Programming languages, version control and problem-solving | Microsoft Certified Azure Developer Associate, Certified Kubernetes Administrator, Oracle Certified Java Programmer |
Data Science and Analytics
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Data Scientists, Data Analyst, Machine learning engineer, business intelligence analyst | Data analyzation, creating machine learning models, data visualization | Statistical analysis, machine learning, programming | Microsoft Certified Data Analyst Associate, Certified Analytical Professional, SAS Certified Data Scientist. |
Cybersecurity
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Cybersecurity Analyst, Ethical Hacker, Network Security Engineer, Information security Manager | Protecting System from Cyber threats, Risk Assessment, and ensuring compliance | Network security, encryption, threat modeling. | CompTIA Security+, Certified Information System Security Professional, Certified Ethical Hacker |
Cloud Computing and DevOps
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Cloud engineer, Cloud architect, DevOps Engineer | Cloud Infrastructure management, cloud integration management, deploying applications | Cloud platforms tools, scripting, DevOps Tools and automation. | AWS Certified Solution Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals, Google Associate Cloud Engineer |
Network and System Administration
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Network Administrator, System Administrator, Network Engineer. | Managing computer network, troubleshooting and network security | Network protocols, Linux, Windows OS, Cloud infrastructure. | Cisco Certified Network Associate, Cisco Certified Network Professional, CompTIA Network+ |
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| AI engineer, Machine learning engineer, NLP engineer | AI algorithm design, building machine learning models | Network language processing, Neural Network and Deep learning | AWS Certified Machine Learning, Certified Artificial Intelligence Professional. |
Database Administration and Management
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| Database Administrator, Engineer and Architect | Data Base Management, database solutions, Backup and recovery | SQL, database management system, data modeling | Microsoft Certified Azure Data Fundamentals, Oracle Database SQL ,Certified Associate, IBM Certified Database Administrator. |
IT support and Helpdesk
| Roles | Responsibilities | Skills | Certificates |
| IT support specialist, Helpdesk technician, technical support engineer. | Providing technical assistance, setting up systems and supporting users. | Customer service, networking basics, and troubleshooting. | ITIL Foundation, Certified Information System Auditor, Project Management Professional |
Above mentioned are the roles, responsibilities, skills and certificate required for students who want to pursue their careers in information technology field.
Conclusion
Information technology (IT) is an integral part of modern life, driving innovation, efficiency, and connectivity across industries. Its evolution—from the early abacus and mechanical calculators to today’s advanced AI, blockchain, and cloud computing systems—reflects humanity’s quest to enhance data management, communication, and problem-solving. IT not only powers business operations and scientific research but also empowers individuals through education, healthcare, and personal technology.
As the backbone of global communication, IT has transformed how we work, learn, and live. Its applications in data storage, cybersecurity, and networking ensure seamless and secure access to information in real time. Furthermore, the continuous advancements in IT have paved the way for emerging technologies like smart cities, virtual reality, and the Internet of Things, creating opportunities for sustainable growth and innovation.
The career landscape in IT is equally diverse, offering roles in software development, data analytics, cybersecurity, and beyond. With the right skills and certifications, professionals can contribute to shaping the future of this dynamic field. Ultimately, information technology is not just a tool—it’s a foundation for progress in our increasingly interconnected world.
References:
- https://web.archive.org/web/20141226170451/http://www.ee.ryerson.ca:8080/~elf/abacus/intro.html
↩︎ - https://www.meccano.us/difference_engines/rde_1/ ↩︎
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Turing_machine ↩︎
- https://ed-thelen.org/comp-hist/BRL61-ibm03.html#IBM-305-RAMAC ↩︎
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120323162124/http://startup.nmnaturalhistory.org/gallery/item.php?ii=26 ↩︎
- https://www.ukwhoswho.com/display/10.1093/ww/9780199540884.001.0001/ww-9780199540884-e-12699 ↩︎
